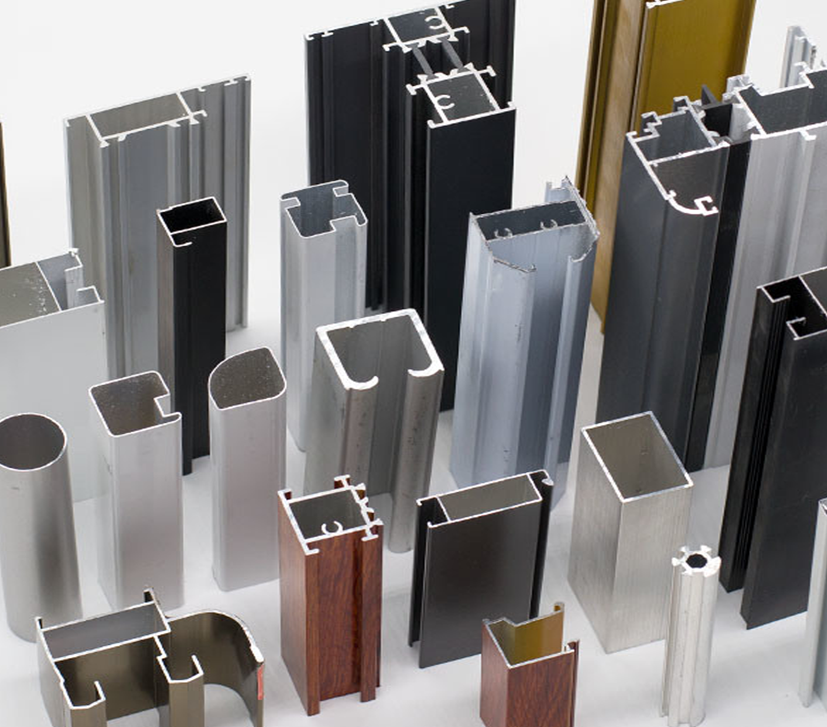
Aluminum
Aluminum is a chemical element with symbol Al and atomic number 13. It is a silvery-white, soft, non-magnetic and ductile metal. Aluminum is the third most abundant element in the earth’s crust, making up about 8% by weight of the crust. It is light, strong and corrosion resistant and is also a good conductor of electricity and heat. It can be easily forged, machined, cast.
Aluminum Types and Usage Areas
There are several types of aluminum, including:
Pure Aluminum
This is aluminum in its purest form, with a purity of 99.0% or higher. It is soft and ductile and is often used for electrical conductors, decorative applications and chemical processing equipment.
Alloy aluminum
It is aluminum combined with other elements to improve its properties. Common alloying elements include copper, zinc, magnesium and silicon. Different types of alloyed aluminum are used for different purposes such as strengthening, corrosion resistance, and electrical conductivity. Some common types of alloyed aluminum and their uses include:
2024 alloy:
It is a high strength aluminum alloy used for aircraft components in the aerospace industry.
5052 alloy
It is a medium strength alloy used in the shipping and construction industries for applications such as airframes, automotive bodies and architectural extrusions.
6061 alloy
This is a medium strength alloy commonly used in the transportation and construction industries for applications such as bicycle frames, structural components and truck bodies.
7075 alloy
It is a high strength alloy used in the aerospace industry for aircraft components, in the defense industry for armor plates and other applications.
In addition to these types of aluminum, there are many other alloys used for certain applications, such as marine grade aluminum for use in marine environments and food grade aluminum for use in the food processing industry.
Some of the applications used are as follows:
• Power lines
• Tall buildings
• Window frames
• Consumer electronics
• Home and industrial devices
• Aircraft components
• Spacecraft components
• Ships
• Trains
• Personal vehicles etc.