- +90 216 912 14 74
- info@paftamuhendislik.com.tr
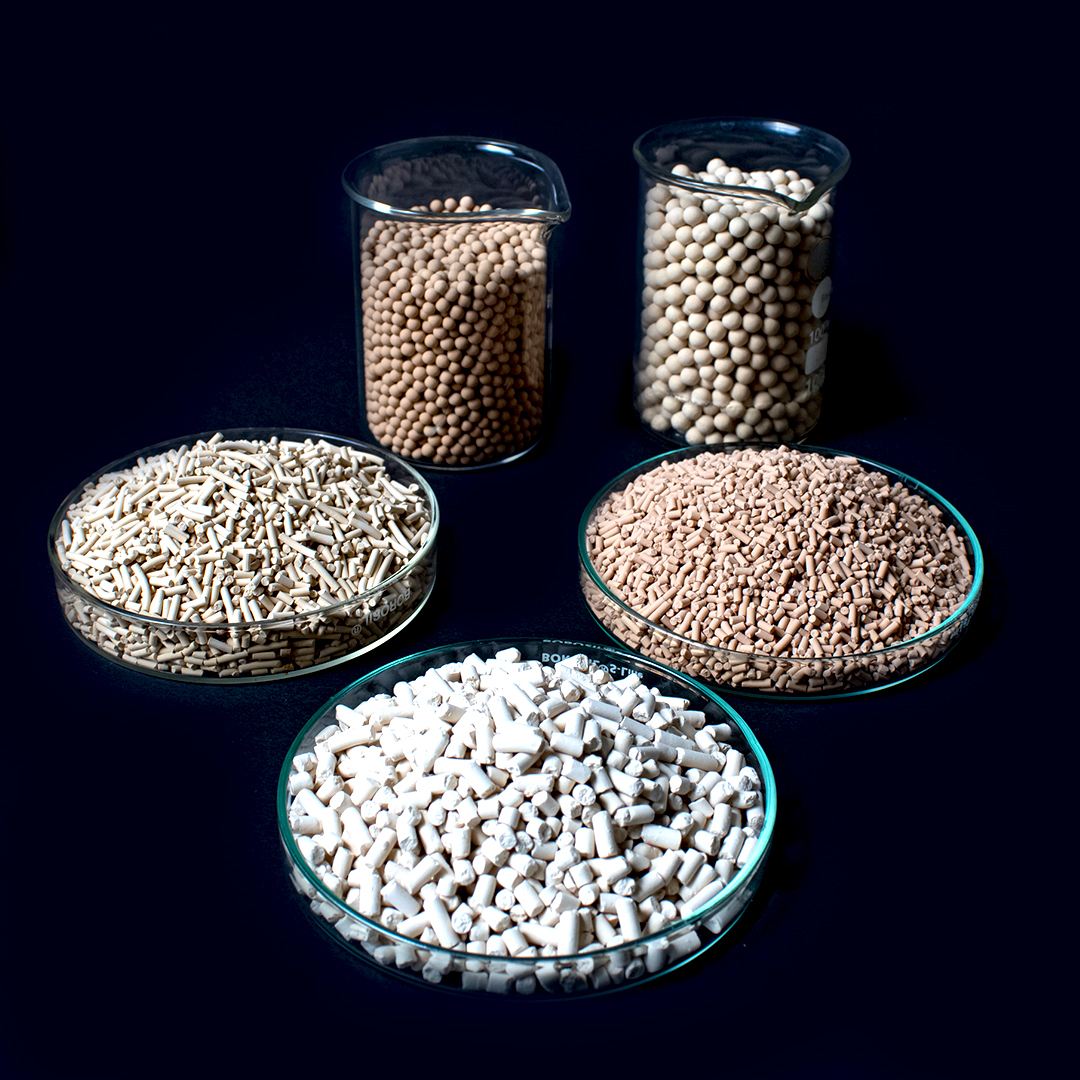
- Welcome to Pafta Mühendislik San. İç ve Dış Ticaret


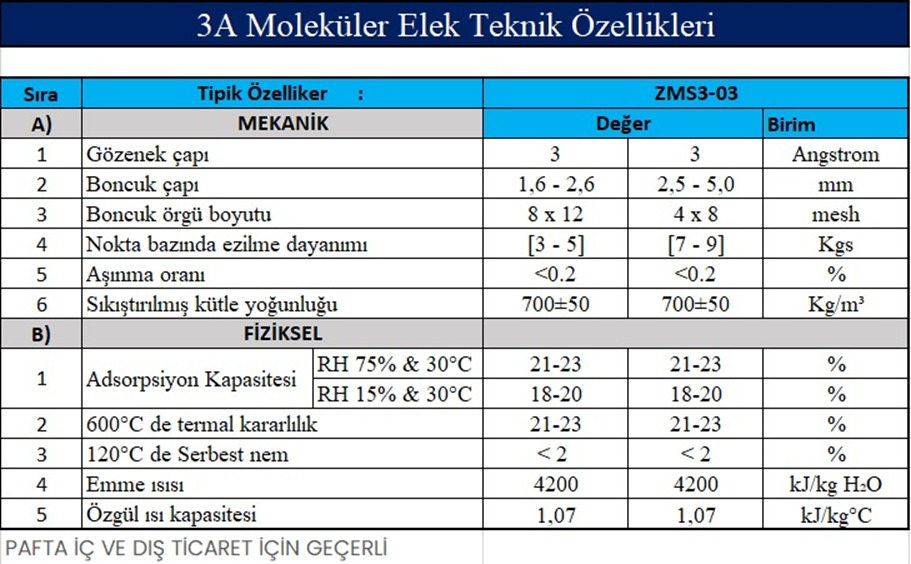
3A (potassium type A):
3A molecular sieve mainly;
oil cracking gas
olefin
refinery gas
Besides oilfield gas
It is used to dry a desiccant in the chemical, pharmaceutical, insulating glass and other industries.
It is mainly used in gas drying, refrigerant drying, etc., where liquids (such as ethanol) are dried, insulating glass is air dried, mixed with nitrogen and hydrogen.

4A (sodium type A)
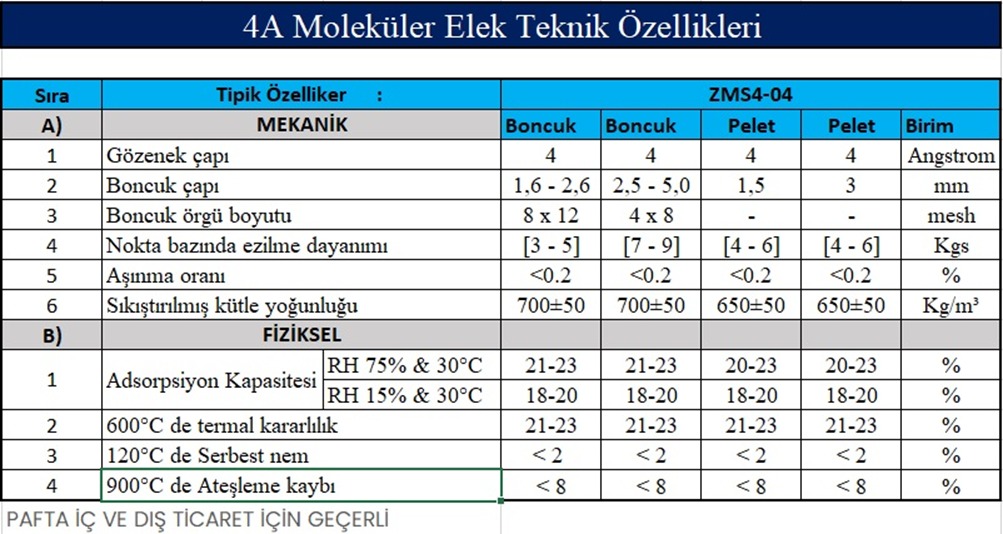
4A molecular sieves mainly;
Natural gas and various chemical gases and liquids
of refrigerants
of pharmaceuticals
Drying of electronic data and volatile substances
It is used for purification of argon and separation of methane, ethane and propane.
Mainly used for deep desiccant of gases and liquids, such as air, natural gas, hydrocarbons, refrigerants; preparation and purification of argon, static dryer of electronic components and perishable materials; dewatering agent in paints, polyesters, paints and coatings.

5A (calcium type A)
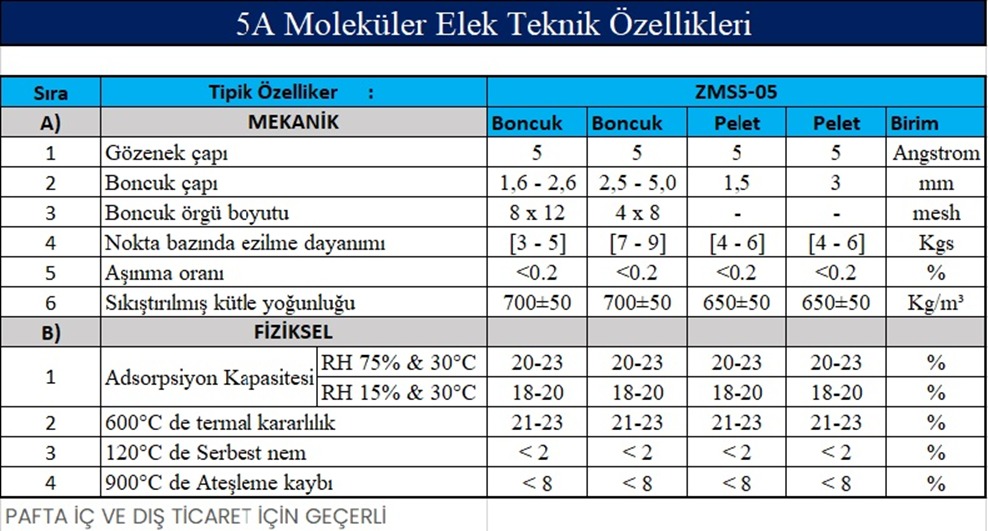
5A molecular sieve mainly;
natural gas drying
It is used for desulfurization and carbon dioxide removal.
Separation of nitrogen and oxygen to prepare oxygen, nitrogen and hydrogen; dewaxing of petroleum to separate normal hydrocarbons from branched hydrocarbons and cyclic hydrocarbons.

13Z (sodium Z type)
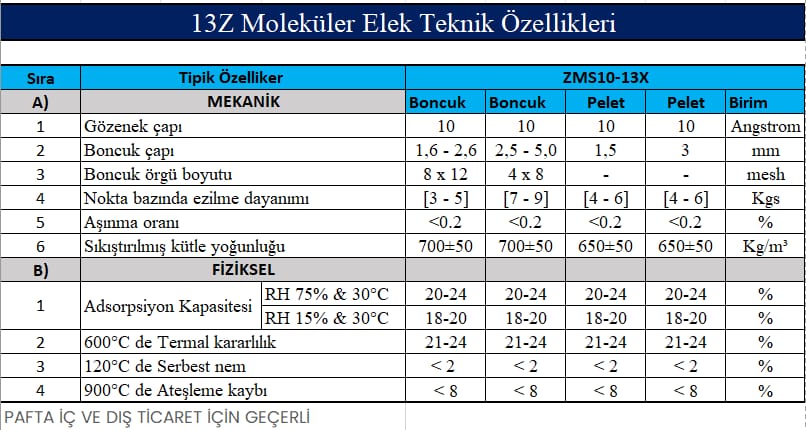
13x is mainly used in:
Gas purification in air separation unit to remove water and carbon dioxide.
Drying and sulphurisation of natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas and liquid hydrocarbons.
General gas deep drying.

Whatsapp İletişim