Fertilizer
Fertilizers are food for plants: they provide nutrients for the growth and development of plants. A mineral plant nutrient is essential or beneficial for plant growth and development, or essential for the quality characteristics of the harvested product grown in the natural or cultivated environment of a particular plant species. They typically contain one or more essential plant nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. Fertilizers can be organic, that is, they are made from naturally occurring materials, or they are made synthetic, that is, from chemicals.
Types of fertilizers
Fertilizer types are divided into natural (organic) and artificial according to their structure:
Organic (Natural) Fertilizers
Fertilizers obtained from plants and animals are called organic fertilizers. They do not harm seeds and sprout roots as they are slower acting and less soluble in water. For this reason, they are more preferred in vegetables and flowers. Another feature of organic fertilizers is that they increase the rate of organic matter in the soil and regulate the physical properties of the soil. The most important types of organic fertilizers; barnyard manure, compost and green manure.
Artificial Fertilizers
Nitrogen fertilizers: These fertilizers contain nitrogen necessary for the growth of leaves and stems. Nitrogen fertilizers are generally used in lawns and gardens.
Phosphorus fertilizers: These fertilizers contain phosphorus, which is essential for root growth and flower and fruit production. Phosphorus fertilizers are generally used on flowers, fruit trees and vegetables.
Potassium fertilizers: These fertilizers contain potassium, which is important for overall plant health and strong root and stem development. Potassium fertilizers are generally used on fruit trees and vegetables.
Compound fertilizers: These fertilizers contain a combination of two or more essential plant nutrients. They are often used on a wide variety of plants, including flowers, vegetables, and grasses.
Usage areas
Fertilizers are used in agriculture, horticulture and landscaping to improve soil fertility and increase crop yields. They are typically applied to the soil before planting or during the growing season to provide essential nutrients to the plants. In agriculture, fertilizers are used to grow a variety of crops, including grains, fruits, vegetables, and nuts. They are often applied to fields in large quantities and are an important part of modern agricultural practices.
In horticulture, fertilizers are used to grow ornamental plants such as flowers, shrubs and trees. They are also used to maintain the health and appearance of lawns and gardens. Fertilizers are used in landscaping to maintain the health and appearance of public and private spaces, including parks, golf courses, and home gardens.
Fertilizers can be applied using a variety of methods, including manual spreading, broadcasting and injection. The specific method and timing of fertilizer application will depend on the type of plants being grown and the needs of the soil. Fertilizers are used in agriculture, horticulture and landscaping to improve soil fertility and increase crop yields. They are also used to maintain the health and appearance of lawns, gardens and other landscaped areas.
Fertilizer Types in Pafta Engineering
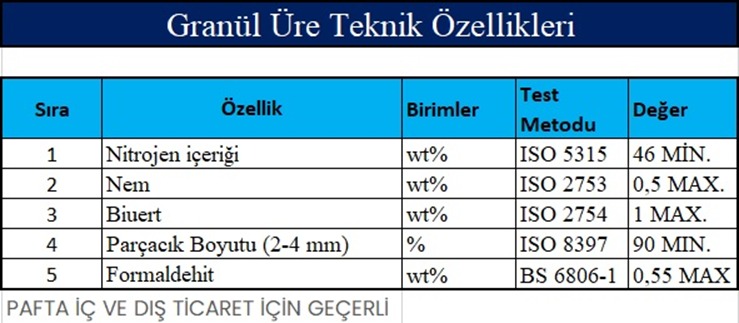
UREA (46%N)
Urea is the most important nitrogen fertilizer on the market, with the highest Nitrogen content (about 46 percent). It is a white crystalline organic chemical compound. Urea is neutral in pH and can adapt to almost any type of soil. As in humans, it is a naturally occurring waste product by metabolizing protein in other mammals, amphibians and some fish. Urea is widely used as both fertilizer and animal feed additive in the agricultural sector.
The main function of urea fertilizer is to provide plants with nitrogen to promote leafy green growth and keep plants looking bushy. Urea also aids in the photosynthesis process of plants. Since urea fertilizer can only provide nitrogen and not phosphorus or potassium, it is primarily used for flower growth.
Advantages of Urea Fertilizer
o Superior Nitrogen content
o Low production cost as the source is natural
o Fireproof and risk-free storage
o Wide application range for all types of crops and soils
o Neutral pH and harmless to crops and soil
Urea Fertilizer Use
1-Urea should be applied during planting. It should not come into contact with the seeds. It can also be applied as a top dressing.
2- Since urea has a high nitrogen concentration, it should be used with soil or sand before application.
3- Urea should not be applied when the soil contains free water or is likely to remain wet for three or four days after application.
Tips for Mixing Urea with Other Fertilizers
Urea can be easily mixed with Mono-ammonium Phosphate (MAP) or Di-ammonium Phosphate (DAP). However, because Urea reacts with water molecules releasing superphosphate, Urea should not be mixed with any superphosphate unless applied immediately after blending. This will produce a moist material that is difficult to store and apply